√無料でダウンロード! exocrine glands diagram 720774-Exocrine glands diagram
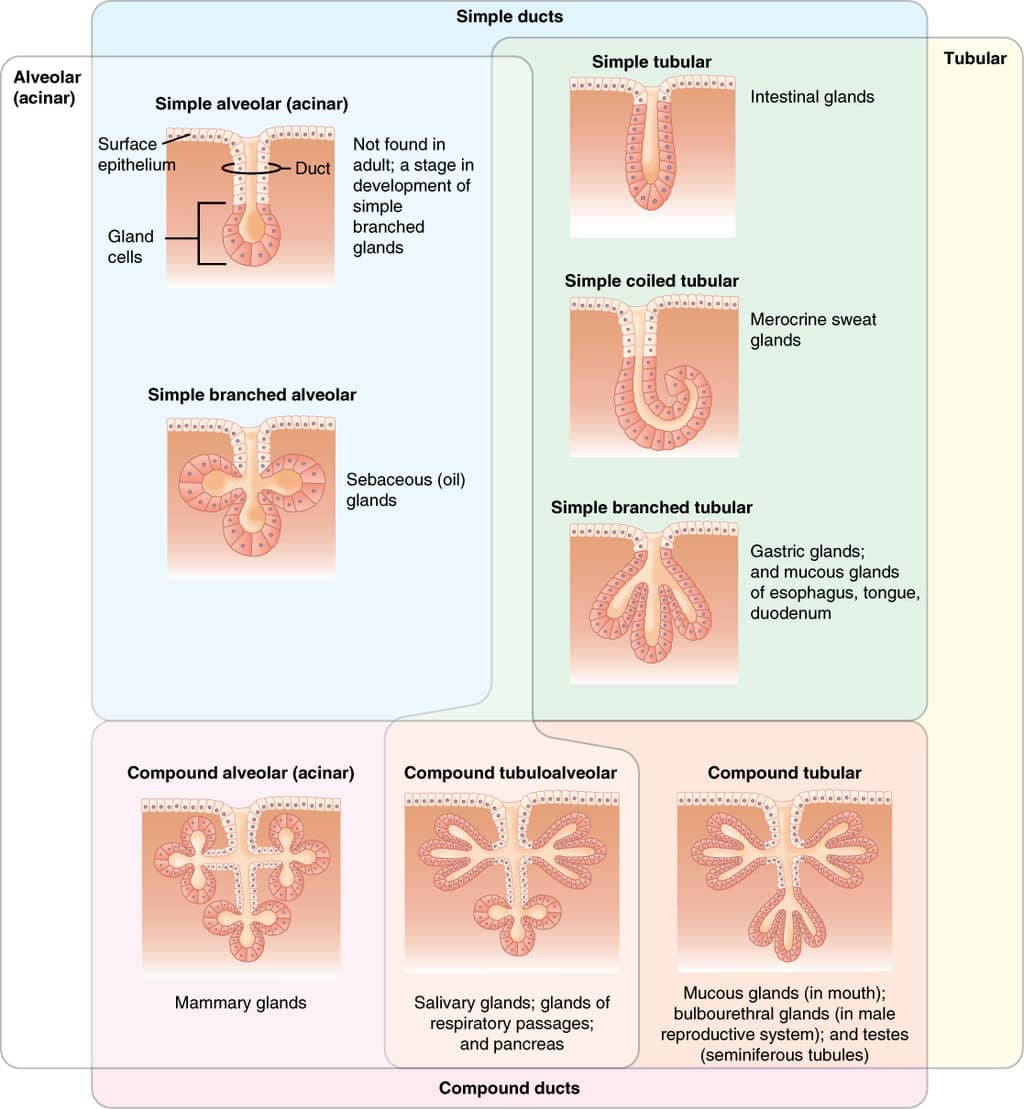
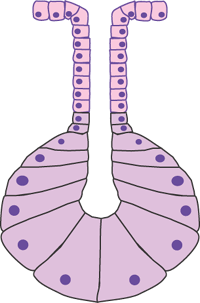
Exocrine pancreas pancreas serous tubuloacinar Gastric chief cell, Wasmann's glands stomach serous Glomus coccygeum, coccygeal gland, Luschka's gland or gangliona coccyx, near the tip Goblet cells digestive tract, respiratory tract mucous simple unicellular Henle's glands eyelids, in the conjunctiva tubular Krause's glands conjunctiva, middle portion Question Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the structural classification of exocrine glands Res Compound Dubular Simple coiled Oland Compound Alveolar (acinar) Simple tubular Simple branched hiver Simple branched Simple alveo Exocrine glands remain connected to the covering epithelium via tubular ducts which are lined with lining epithelium and carry the secreted products into the site of action The effects of exocrine gland secretions are limited, and some of them would be
Exocrine Glands
Exocrine glands diagram
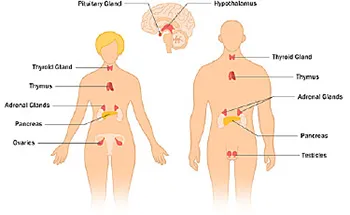
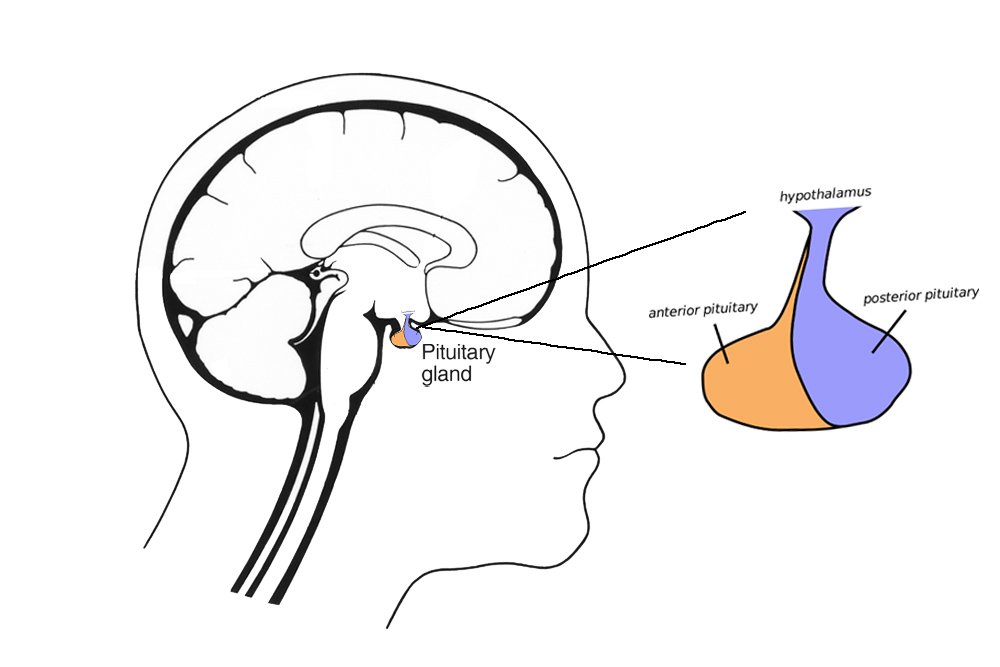
Exocrine glands diagram-Chapter 31 Endocrine Physiology Endocrine Anatomy & Physiology GLAND LOCATIONS & FUNCTIONS Endocrine glands scattered throughout body Hypothalamus Located at base of brain Hypothalamus, brain work closely to make hormones that control other endocrine glands Made up of several nuclei (neuron clusters) which secrete hormones Pituitary gland Located just below Endocrine Gland Diagram Written By JupiterZ Friday, Add Comment Edit Endocrine System Sheep Human Endocrine Glands With Picture Endocrine Vs Exocrine Glands Difference Endocrine Gland Diagram Labeled Wiring Diagram T4 Introduction Of Endocrinology Important To Know Glandular




Glands Classifications Types Functions And Diagrams Jotscroll
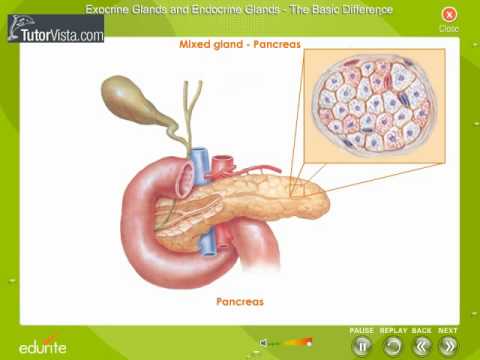
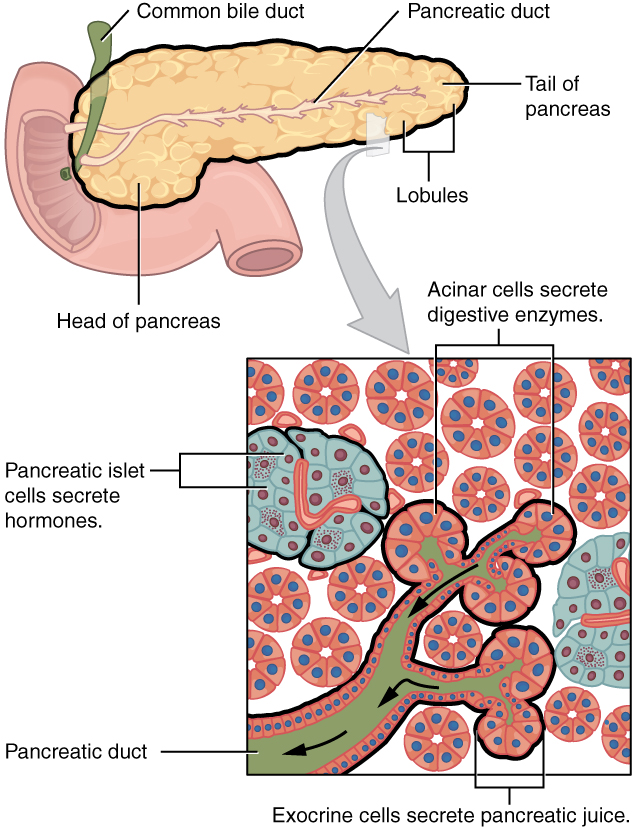
Well Labelled Diagram of the General structure of Exocrine Glands Multicellular Glands An example of multicellular exocrine gland is the secretory sheet of the epithelial lining of the stomach of which the cells form a continuous epithelial layerThere are over major hormones that are pumped into the bloodstream directly by the endocrine system glands This system organs consists of the following glands in human begins Hypothalamus;As in salivary glands, intercalated ductal cells in the pancreas contribute bicarbonate ions (sodium and water follow passively) to the exocrine secretory product However, unlike salivary glands, there are no striated ducts in the pancreas to recover sodium, so the final product is rich in both sodium and bicarbonate (as opposed to saliva in which the sodium content is about one tenth
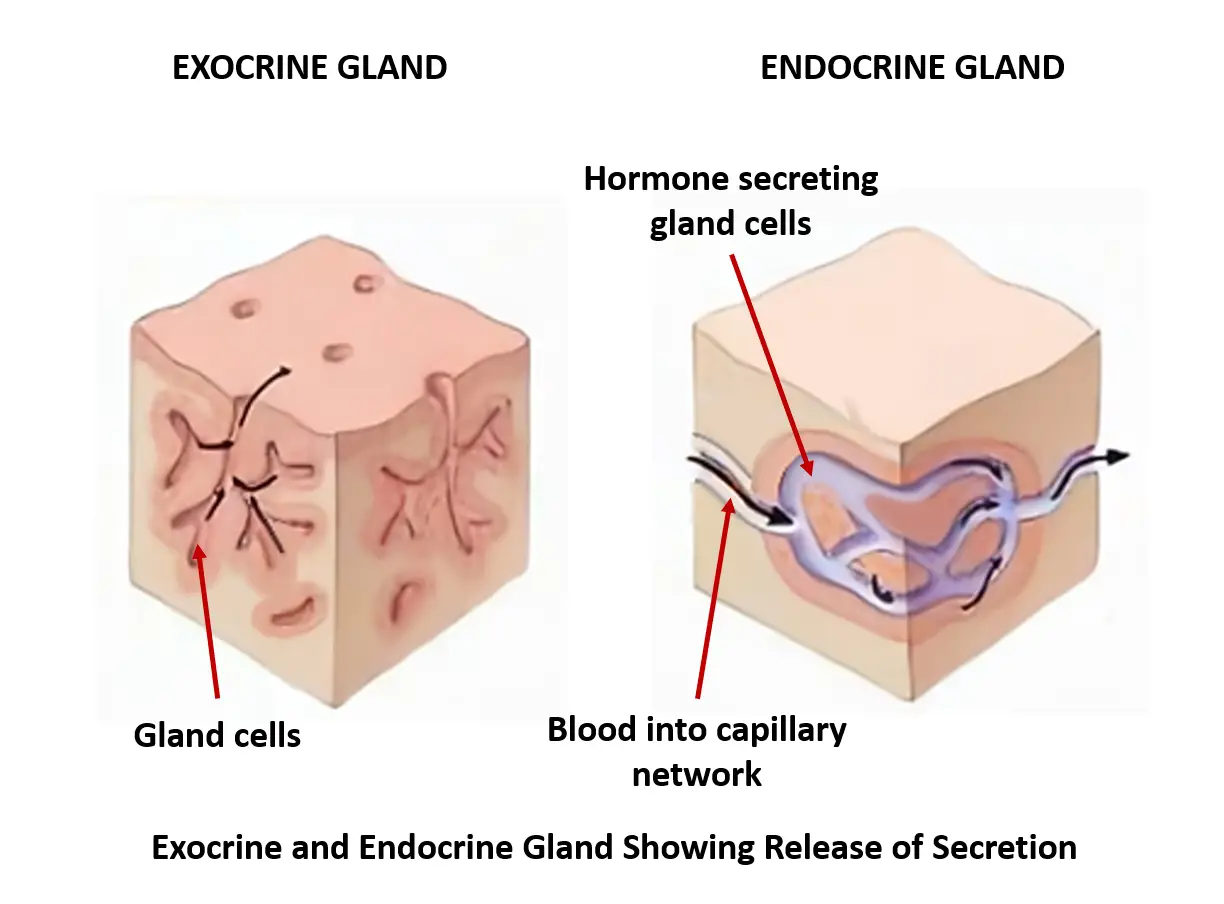
Exocrine Glands Exocrine glands have ducts and they secrete onto a surface examples of exocrine glands are sebaceous and sweat glands (in the skin), salivary glands (oral), Brunner's glands So, we have covered their basic structure and function in tissue types, and we have looked at several examples of exocrine glands in other topicsExocrine system is one of the two types of gland systems in our body It is a collection of glands Exocrine system produces and secretes substances that are necessary to protect and lubricate the human body Exocrine glands are composed of a glandular portion and a duct portionExocrine glands secrete chemical substances into ducts that lead either to other organs or out of the body ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) stimulates secretion of steroid hormones by adrenal cortex ADH (antidiuretic hormone) secreted by the posterior pituitary gland, it increases water reabsorption in the kidneys
Finden Sie perfekte Illustrationen zum Thema Exocrine Gland von Getty Images Wählen Sie aus erstklassigen Bildern zum Thema Exocrine Gland in höchster QualitätSalivary glands, esophagus, and oral cavity exocrine gland stock illustrationsSearch from Endocrine Glands Diagram Pics stock photos, pictures and royaltyfree images from iStock Find highquality stock photos that you won't find anywhere else



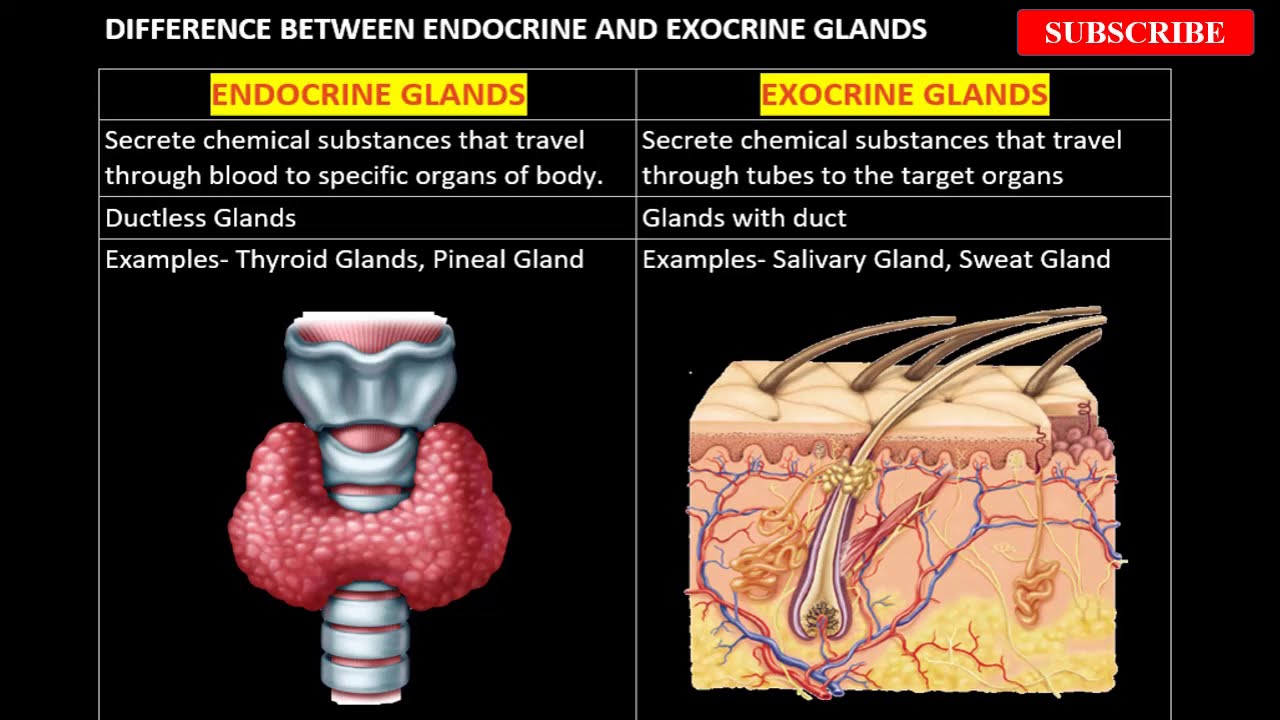
Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Difference Guru



The Endocrine System And Glands Of The Human Body Function And Disorders
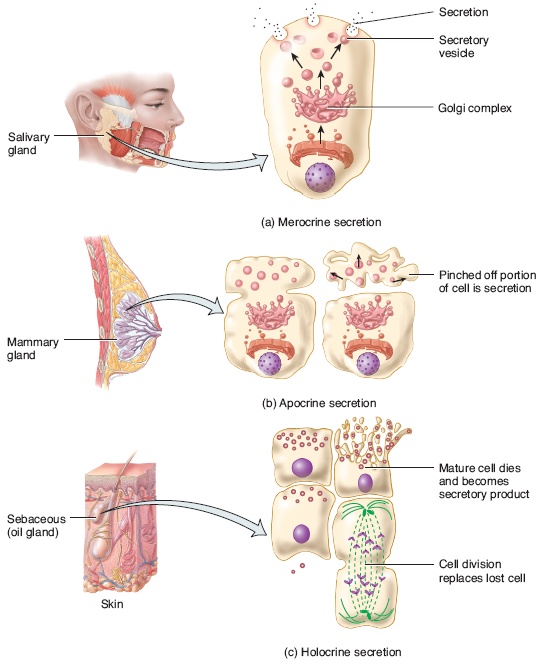
GLANDS Dr Maryam Fatima Demonstrator Anatomy Department We use your LinkedIn profile and activity data to personalize ads and to show you more relevant adsDefine exocrine glands exocrine glands synonyms, exocrine glands pronunciation, exocrine glands translation, English dictionary definition of exocrine glands Sweat glands and other glands that release their products through ducts to a surface or cavity Three types of exocrine glands can be identified based on the mode of secretion merocrine glands, apocrine glands, and holocrine glandsThe merocrine glands secrete their own cellular products The apocrine glands gather the cellular products on the top surface of each cell in the gland and later forms the gland's lumen All cells of the gland are involved in the secretion




Exocrine Glands Bioninja




Exocrine Gland Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Exocrine glands release their contents through a duct that leads to the epithelial surface Mucous, sweat, saliva, and breast milk are all examples of secretions from exocrine glands They are all discharged through tubular ducts Secretions into the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract, Human Exocrine Glands Exocrine secrete into a location or region of the body through a duct and their secretions are called enzymes mostly, while some are nonenzymes Example Sweat Glands, Salivary Glands, Mammary Gland, Ceruminous Gland, Lacrimal Gland, Mucous Gland They perform the following functions Regulate body temperature; 1 A gland having endocrine as well as exocrine function is (a) pituitary (b) thyroid (c) pancreas (d) adrenal;




401 Exocrine Gland Photos And Premium High Res Pictures Getty Images




Overview Of Exocrine Gland Physiology Pancreatic And Salivary Glands The Gastrointestinal System Medical Physiology 3rd Edition
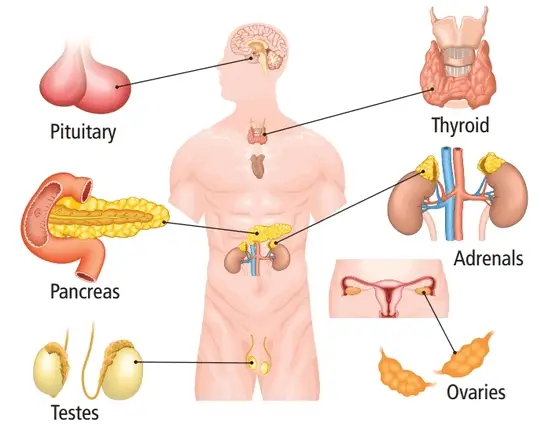
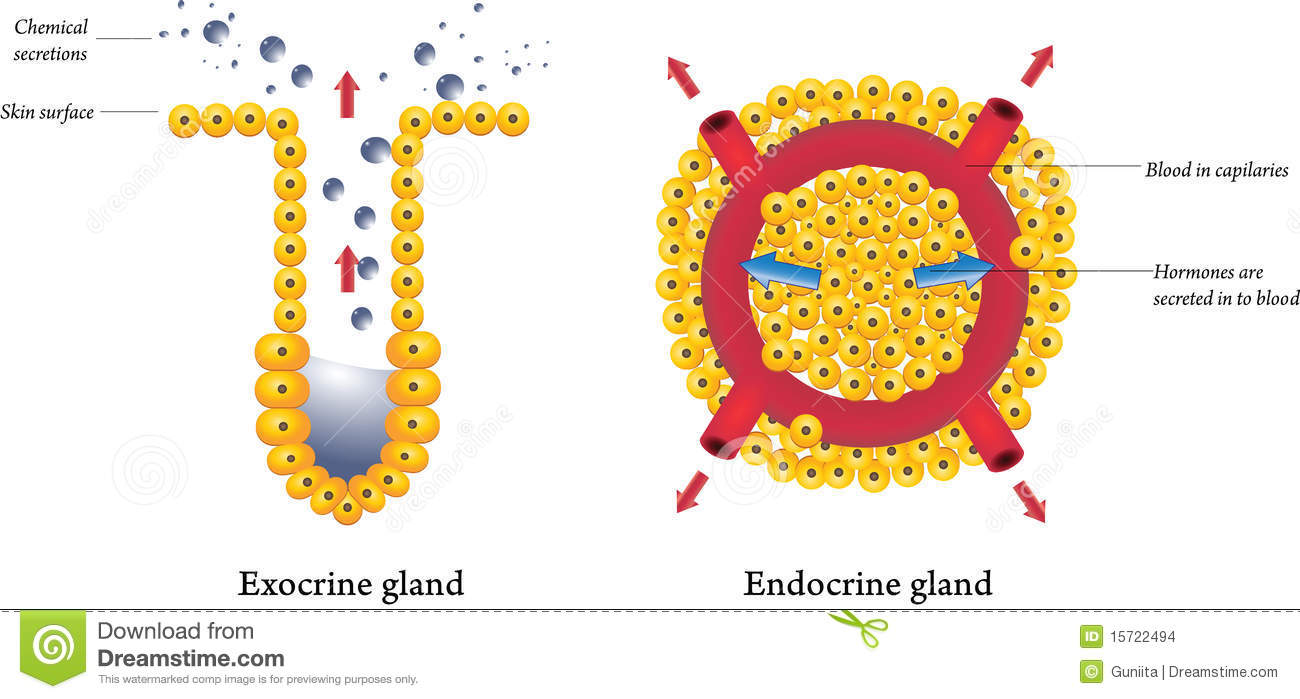
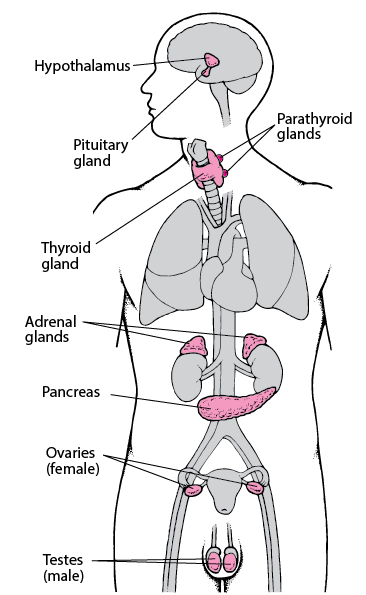
1Conversely, exocrine glands (eg, sweat glands and salivary glands) release their secretions to the outside of the body (eg, sweat) or into a hollow space that is open to the outside (eg, saliva released into the mouth) Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Thyroid gland Parathyroid gland Testis (in male) Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) AdrenalSalivary glands are made up of secretory acini (acini means a rounded secretory unit) and ducts There are two types of secretions serous and mucousThe acini can either be serous, mucous, or a mixture of serous and mucous A serous acinus secretes proteins in an isotonic watery fluid A mucous acinuss secretes secretes mucin lubricant In a mixed serousmucous acinus, the 15 Types of Glands in Human Body & their Functions Glands are the secretory organs in human anatomy They are saclike structures consisting of secretory tissue Exocrine glands Salivary, mucous, lachrymal, pancreatic, ceruminous glands ie sweat glands, and mammary glands Endocrine glands Pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal



Structure Of Glands Exocrine Endocrine Histology Teachmephysiology




Pin On Part I Study Guide
Difference # Exocrine Gland 1 Exocrine gland are the duct glands They are attached with a specific duct 2 The secretory products are enzymes, mucous and other substance 3 The Secretions are released to the outer surface of the body or to some internal organ through aAns (c) 2 Exophthalmic goitre is caused due to the overactivity of (a) thymus (b) thyroid (c) parathyroid (d) adrenal cortex Ans (b) 3 The deficiency of ADH causes (a) diabetes mellitus (b) diabetes insipidus (c) dwarfism (d) acromegaly;Exocrine Glands are those which release their cellular secretions through a duct which empties to the outside or into the lumen (empty internal space) of an organ These include certain sweat glands, salivary and pancreatic glands, and mammary glands They are not considered a part of the endocrine system




Exocrine Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



Endocrine Vs Exocrine Gland Defintion Functions And Differences
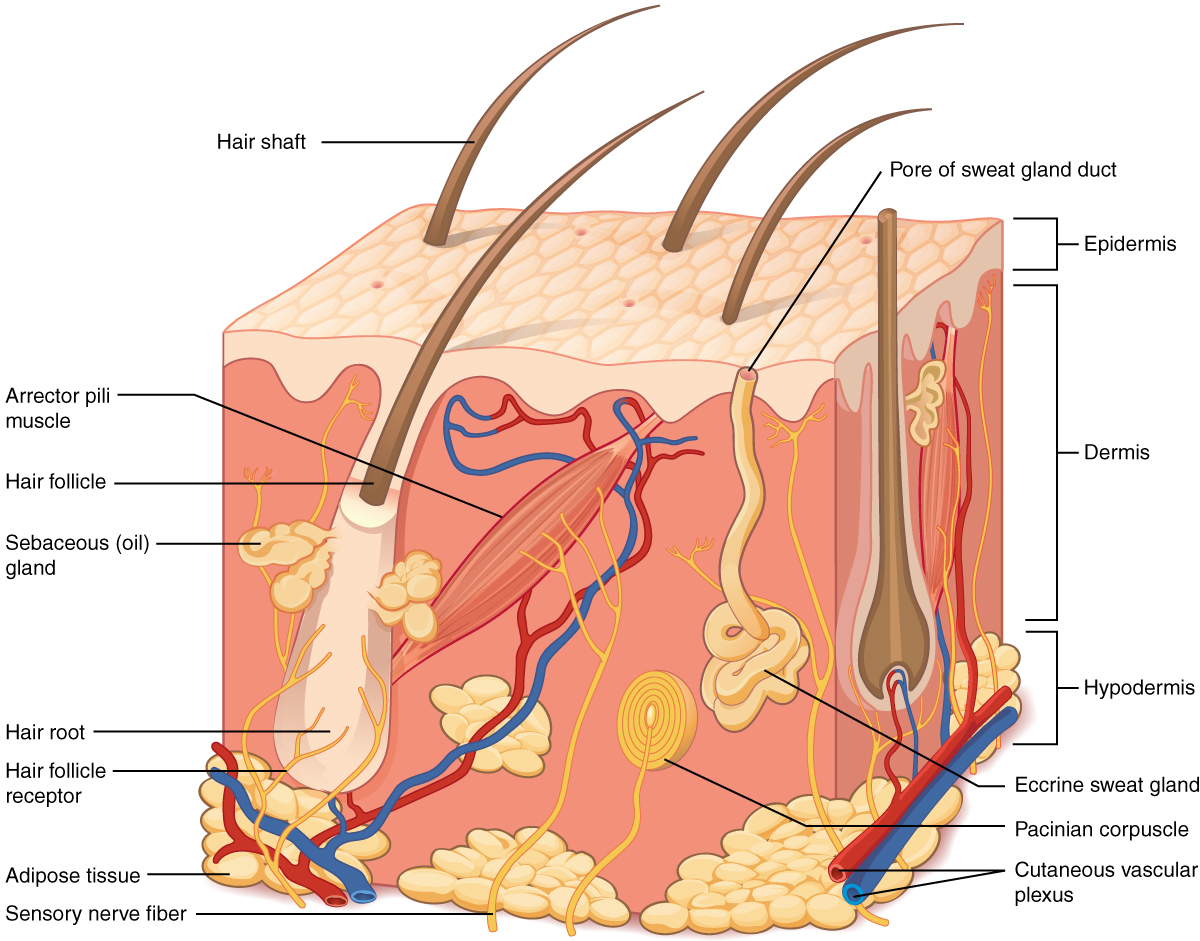
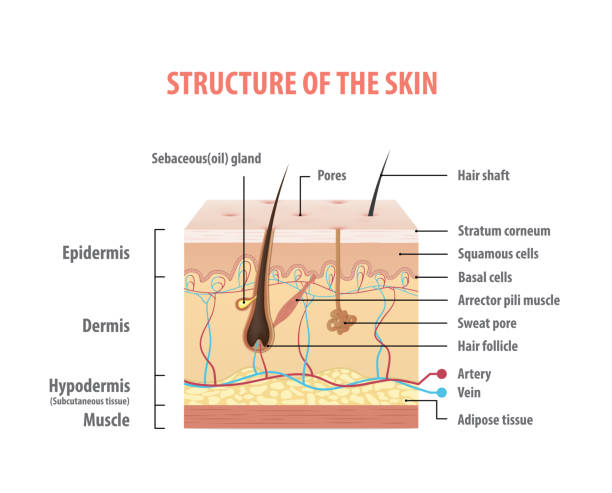
Skin Diagram Oil glands that secrete into the hair follicle An Exocrine gland found in the dermis that secretes its substance through a duct to the surface of the skin Causes the hair to "stand on end" if cold or frightened produces "goose bumps" Students revise some of the essential topics from parts of the SL course so that they are ready to explore the detail of epithelial cells and exocrine glands which are found in different forms all along the gastrointestinal tract The structure of epithelial cells and the adaptations of cells for secretion of mucus or enzymes is covered using a gallery of diagrams and someSearch from Endocrine Glands Diagram Background stock photos, pictures and royaltyfree images from iStock Find highquality stock photos that you won't find anywhere else



Key Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands You Should Know New Health Advisor



Exocrine Vs Endocrine What Is The Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine You Ask We Answer
Diagram illustrating the two layers of human skin, epidermis, dermis and hair follicle exocrine gland stock illustrations medical illustration of the human digestive system;Glands in the human body produce, control and regulate the flow of hormones, breast milk, saliva, and other useful fluids Mental stress influences the flow of hormones and other fluids as well This article explains the significance of glands in metabolism, growth, and reproductionEndocrine Glands vs Exocrine Glands classic Edit this Template Use Creately's easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram, collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats You can edit this template and create your own diagram Creately diagrams can be exported and added to Word, PPT (powerpoint), Excel, Visio or any



Integumentary System Biology For Majors Ii



Glandular Tissue The Histology Guide
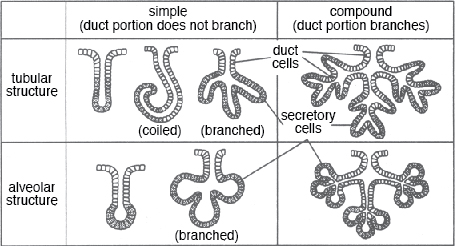
Diagram showing the location of the thyroid gland in the neck The main hormones secreted by the endocrine gland in the pancreas are insulin and glucagon, The exocrine cells secrete pancreatic juices which are used in the duodenum as an important part inLesson Description In this lesson we Differentiate between endocrine and exocrine glands Define a hormone State the location, the hormones secreted and roles of hormones produced by the o Hypothalamus (ADH) o Pituitary/hypophysis (GH, TSH, FSH, LH, prolactin) o Thyroid glands (thyroxin) o Pancreas/islets of Langerhans (insulin,They can either be simple or compound Simple glands these have a single, unbranched duct




Slide 21 Multicellular Exocrine Glands Diagram Quizlet



1 4 Exocrine Gland Stock Photos Pictures Royalty Free Images Istock
Glands are collections of secretory epithelial cells This article discusses the structure of the two main types of glands ( exocrine and endocrine ) Exocrine glands secrete onto a surface and possess 'ducts' lined with epithelium;Islets of Langerhans (Pancreas) Ovaries (Females) Testes (Male) Endocrine System FunctionsExocrine Glands and Endocrine Glands •Exocrine Glands –Exocrine glands have ducts that carry a secretion to a body surface or an organ cavity –Exocrine glands produce extracellular effects –Example sweat glands release sweat onto the skin •Endocrine Glands –Endocrine glands do not have ducts –Endocrine glands release hormones into intercellular




Exocrine Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




The Location Of The Most Commonly Occurring Exocrine Glands In Ants Download Scientific Diagram
Endocrine Glands & Exocrine Glands On the basis of the presence or absence of ducts, the gland is of two typesEndocrine glands – It refers to the glands which secrete their secretions directly into the blood without any duct These are called ductless glands Its target organ can be far away from the source of secretion It can be of two Gland Diagram In this activity, students are going to create a poster that compares the two types of glands found in the skin that are described in the lesson, sweat glands and sebaceous glandsEndocrine system pituitary gland, pineal gland, testicle, ovary, pancreas, thyroid, thymus, adrenal gland Vecto Human endocrine system organs poster Educational horizontal banner for endocrine system or training vector illustration body in plant leaves concept of Human endocrine system vector illustration
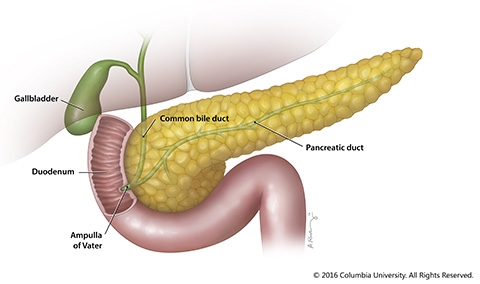



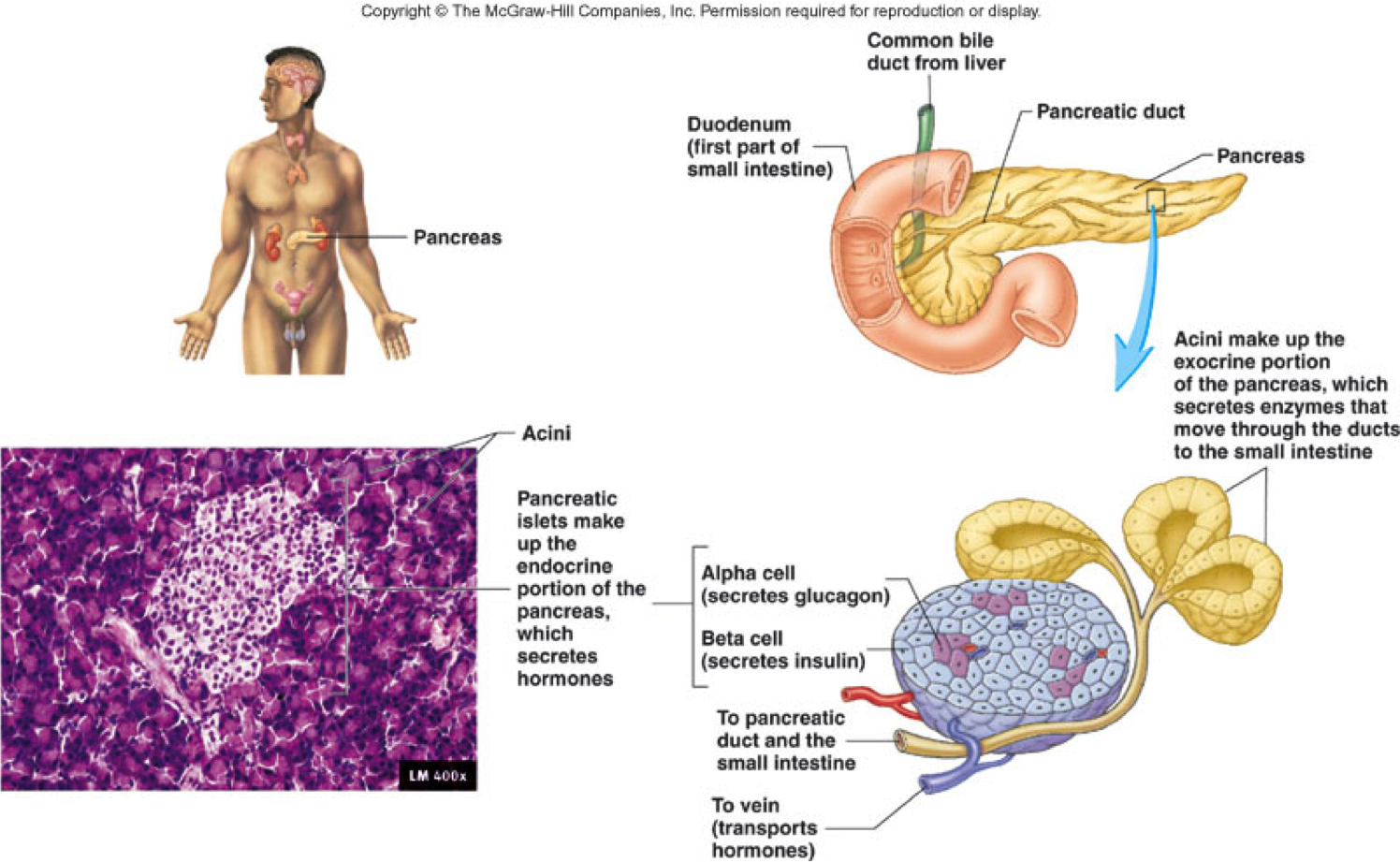
The Pancreas And Its Functions Columbia University Department Of Surgery




Pin On Chapter 5 Histology
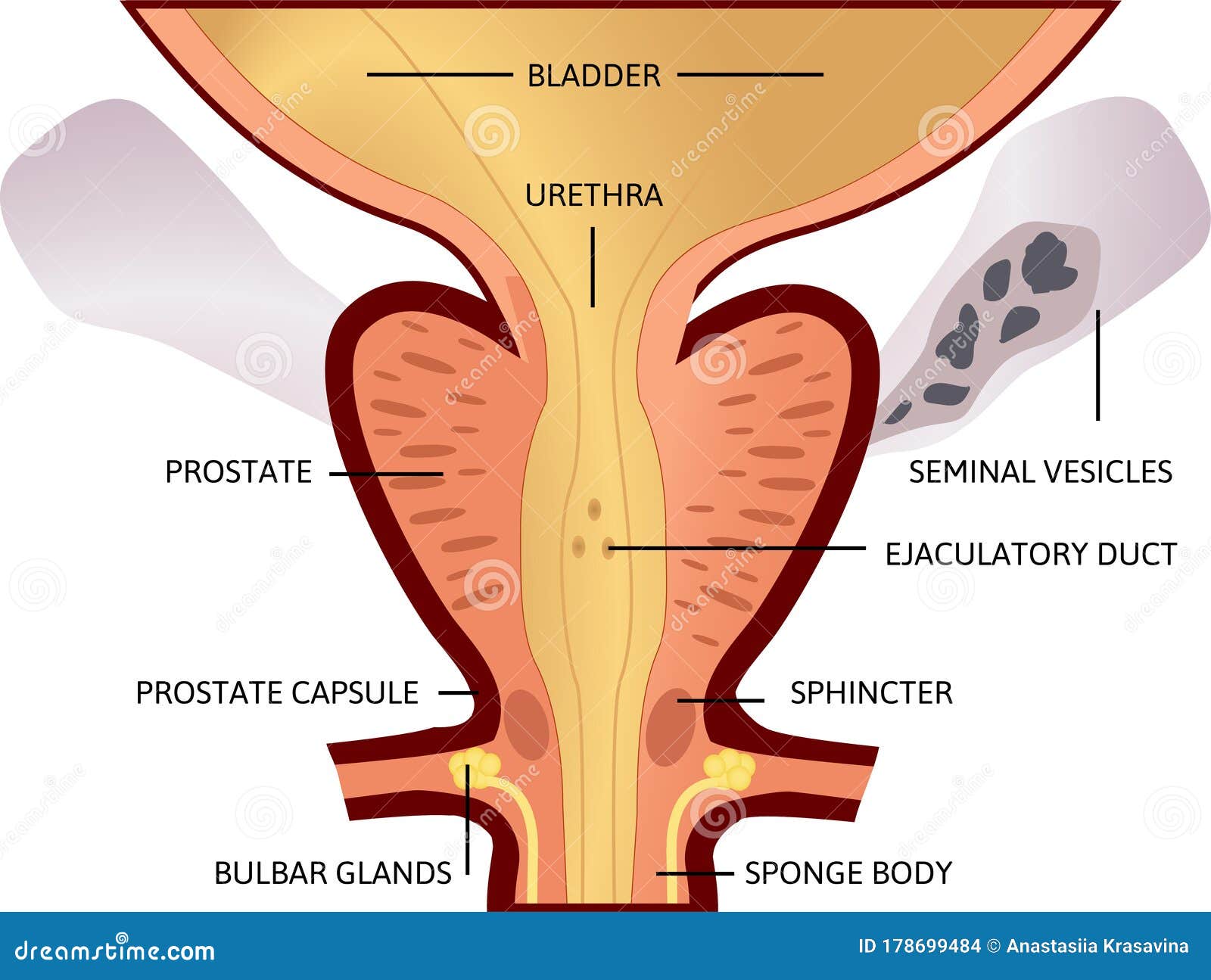
Prostate histology I would like to provide the summary of prostate histology of animal so that you could understand what structures you are going to learn from prostate gland From the prostate histology slide you need to identify the following important structure under light microscope at laboratory – #1 Dense connective tissue capsule of prostate gland of animal
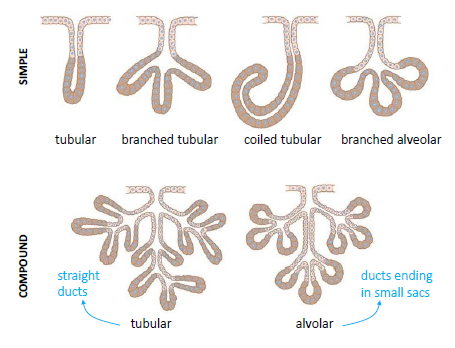



How Are Exocrine Glands Classified Socratic
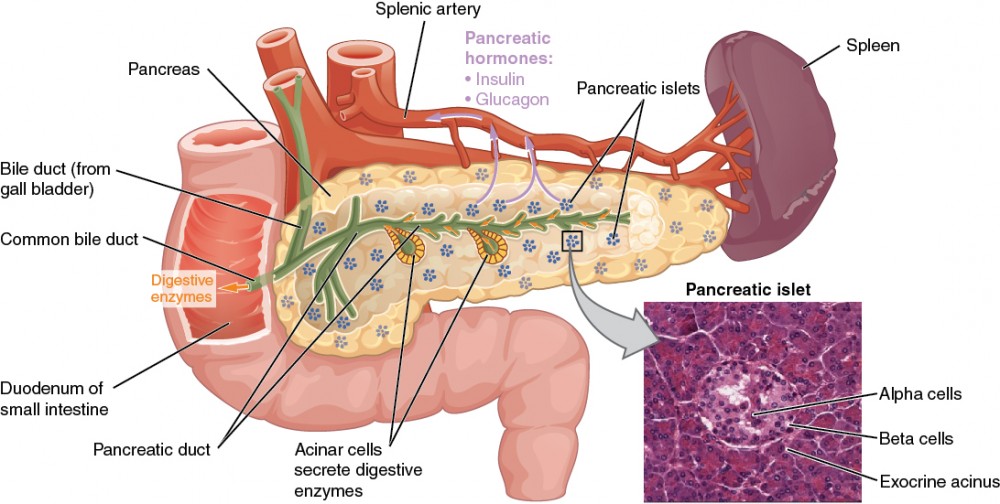



The Endocrine Pancreas Anatomy And Physiology Ii




Schematic Representation Of The Various Types Of Exocrine Skin Glands Download Scientific Diagram




Glands Classifications Types Functions And Diagrams Jotscroll
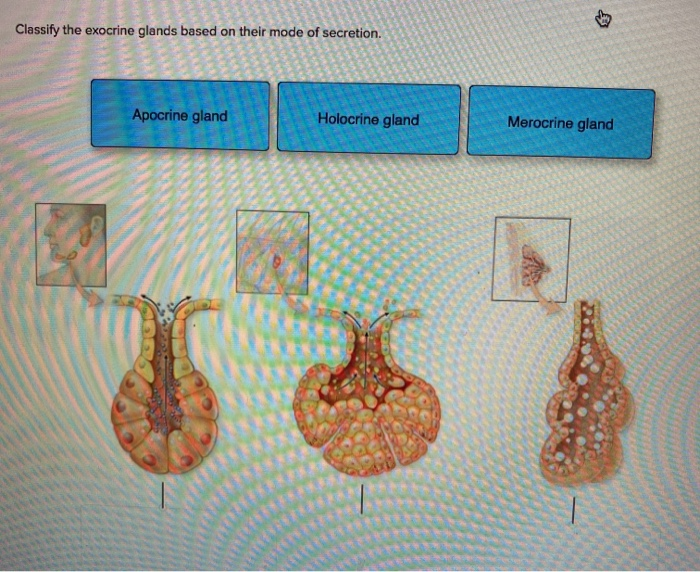



Solved Classify The Exocrine Glands Based On Their Chegg Com
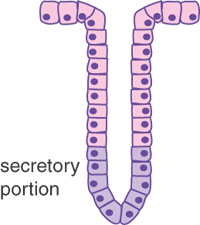



Epithelia The Histology Guide




Learn About Diagram Of Exocrine Gland Chegg Com



Do Any Of The Exocrine Glands Produce Hormones Socratic




Endocrine Glands Definition Examples Function Biology Dictionary



1
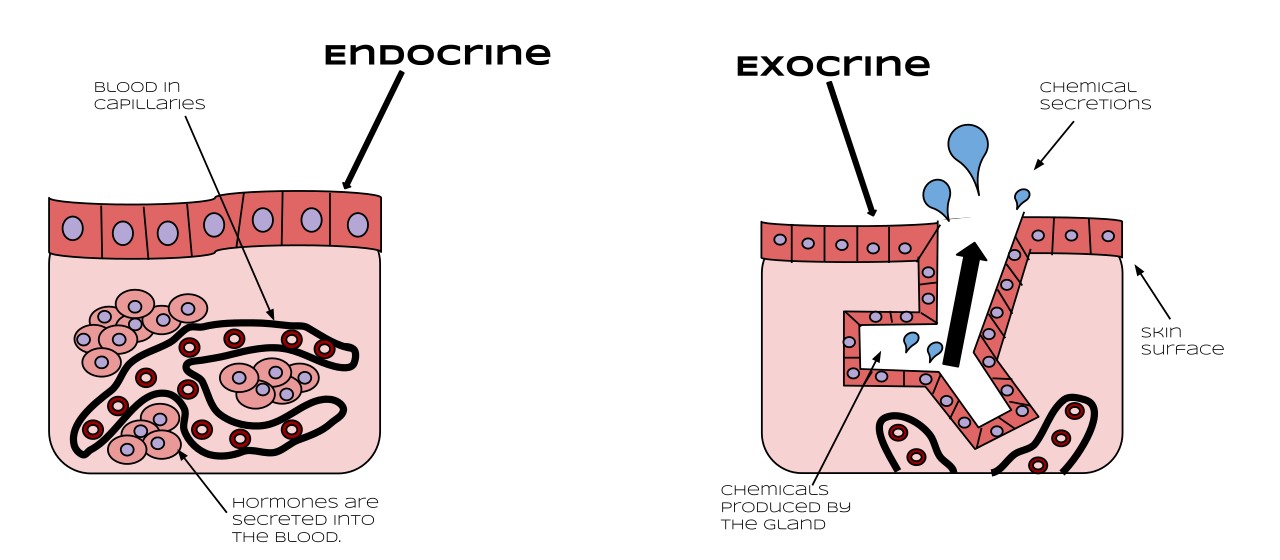



File Endocrine Vs Exocrine Svg Wikimedia Commons
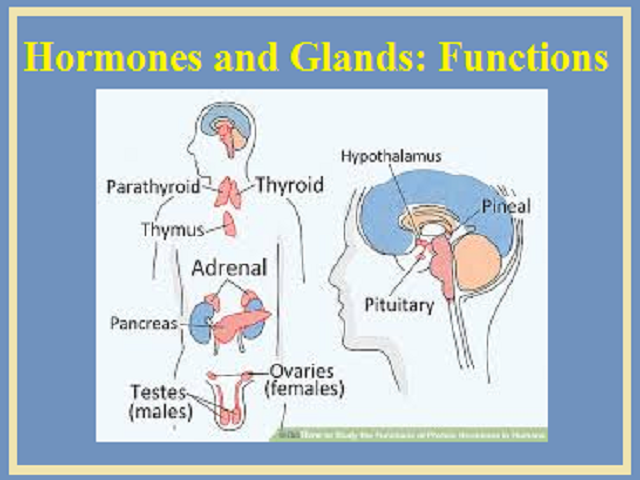



Glands And Hormones In Human Body




Salivary Glands Definition Function And Location Biology Dictionary




Exocrine Gland Cell Of Pancreas Transparent Png 511x275 Free Download On Nicepng



Do Endocrine Glands Secrete Hormones Directly Into The Bloodstream Socratic
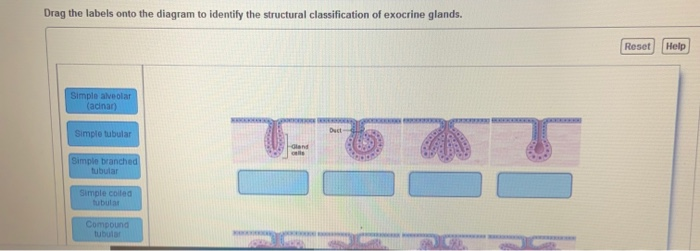



Solved Drag The Labels Onto The Diagram To Identify The Chegg Com




Glands Endocrine Exocrine And Hormones In Human Body



1
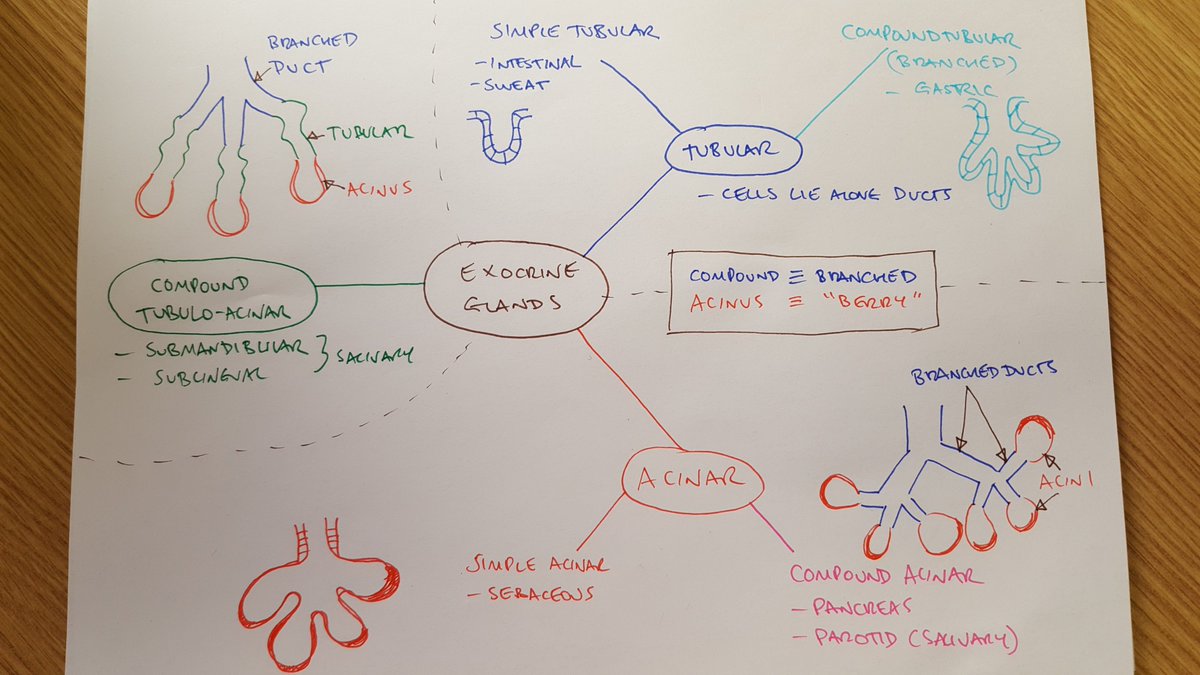



Iain Keenan Here Is My Spider Diagram Of The Classification Of Exocrine Glands For Stage 1 Newcastlemedsch Nme2key




Schematic Diagram Of Green Tree Ant S Exocrine Glands Download Scientific Diagram




Glands Classifications Types Functions And Diagrams Jotscroll
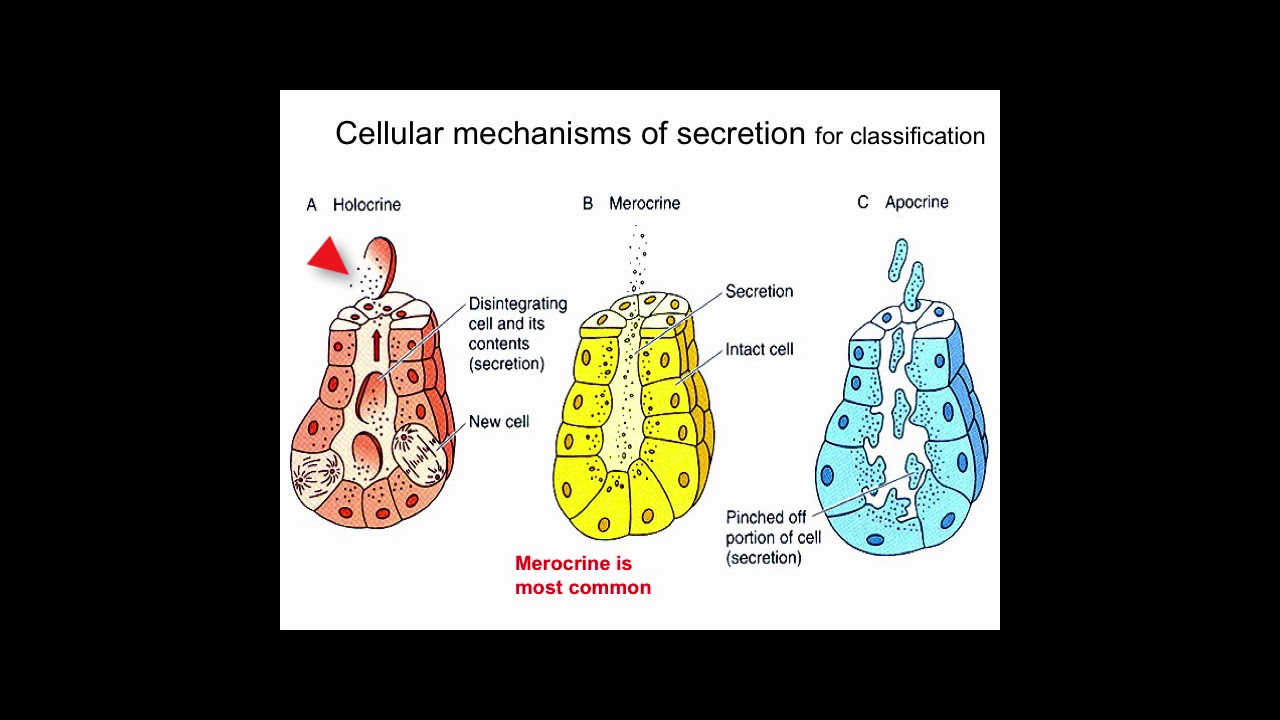



Exocrine Glands Youtube



Epithelia The Histology Guide




Anatomy Of An Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock




Schematic Illustration Of The Arrangement Of The Exocrine Glands In Download Scientific Diagram



Is The Parathyroid An Endocrine Gland Are Sweat Glands Endocrine Glands Socratic




548 Exocrine Gland Illustrations Clip Art Istock




Types Of Glands Definition Examples Diagrams




Exocrine Glands Skin Diagram Diagram Quizlet



Exocrine Gland And Endocrine Glands Youtube




Pineal Gland Endocrine Gland




Glands Classifications Types Functions And Diagrams Jotscroll




Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Differences Function Terms Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Exocrine Gland Wikipedia



Exocrine Glands Classified As Compound Tubular Have What Kind Of Ducts Socratic




Exocrine Gland Structure Physiology Americorps Health



Exocrine Gland Stock Illustrations 157 Exocrine Gland Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Diagram Of The Functional Organization Of The Exocrine Pancreas A The Download Scientific Diagram




Types Of Human Glands Their Secretion Function With Diagram Pdf




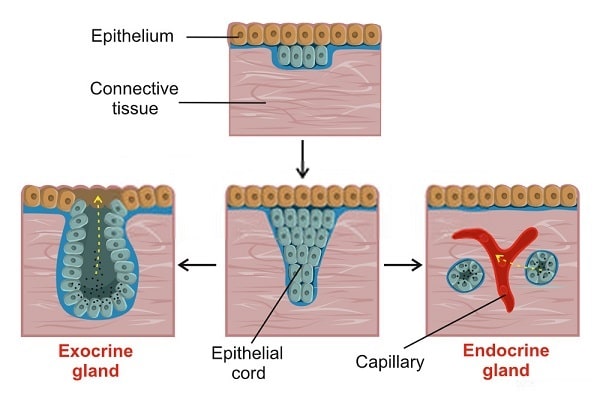
Formation Of Endocrine And Exocrine Glands From Epithelial Sheets Diagram Quizlet




Exocrine Gland Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Human Anatomy Locations Of Multicellular Exocrine Glands Diagram Quizlet




Seer Training Endocrine Glands Their Hormones




Structural Classification Of Exocrine Glands Memory




Labor Related Functional Analysis Of The Three Exocrine Glands Based On Download Scientific Diagram




Survey Of The Exocrine System In Protanilla Wallacei Hymenoptera Formicidae Sciencedirect




Pancreas Exocrine And Endocrine Glands Diagram Poster Zazzle Com




Types Of Glands Definition Examples Diagrams



Exocrine Glands



Endocrine Glands Hormonal And Metabolic Disorders Merck Manuals Consumer Version




Introduction To Endocrine System Basic Definition Examples Diagrams




Endocrine Gland Wikipedia



Epithelia The Histology Guide




Glands Classifications Types Functions And Diagrams Jotscroll




Chapter 4 Review Tissues Multicellular Exocrine Glands Ament Msu Diagram Quizlet



Epithelia The Histology Guide



Pancreas Endocrine And Exocrine Functions Medical Library
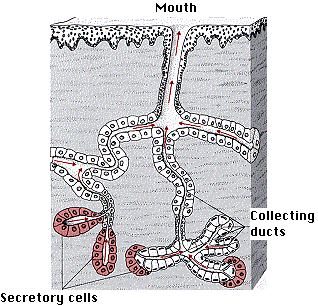



Exocrine Glands
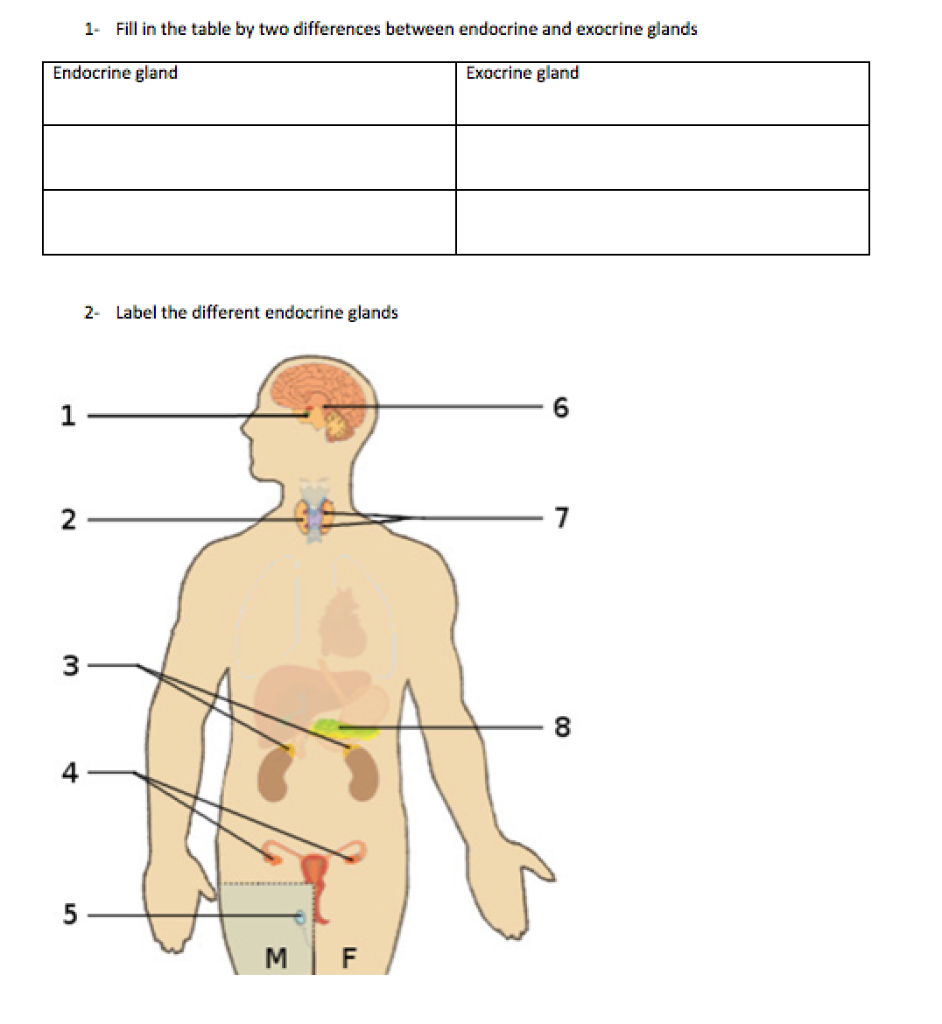



Solved 1 Fill In The Table By Two Differences Between Chegg Com




Schematic Illustration Of The Arrangement Of The Exocrine Glands In Download Scientific Diagram



1




Exocrine Glands Bioninja




Slide Unicellular Exocrine Glands Diagram Quizlet




Exocrine Glands Of The Integumentary System Youtube




Pin On Epithelial Tissue




17 1 An Overview Of The Endocrine System Anatomy Physiology



Plos One Shotgun Proteomics Deciphered Age Division Of Labor Related Functional Specification Of Three Honeybee Apis Mellifera L Exocrine Glands




Endocrine System 1 Overview Of The Endocrine System And Hormones Nursing Times




Multicellular Exocrine Glands Diagram Quizlet
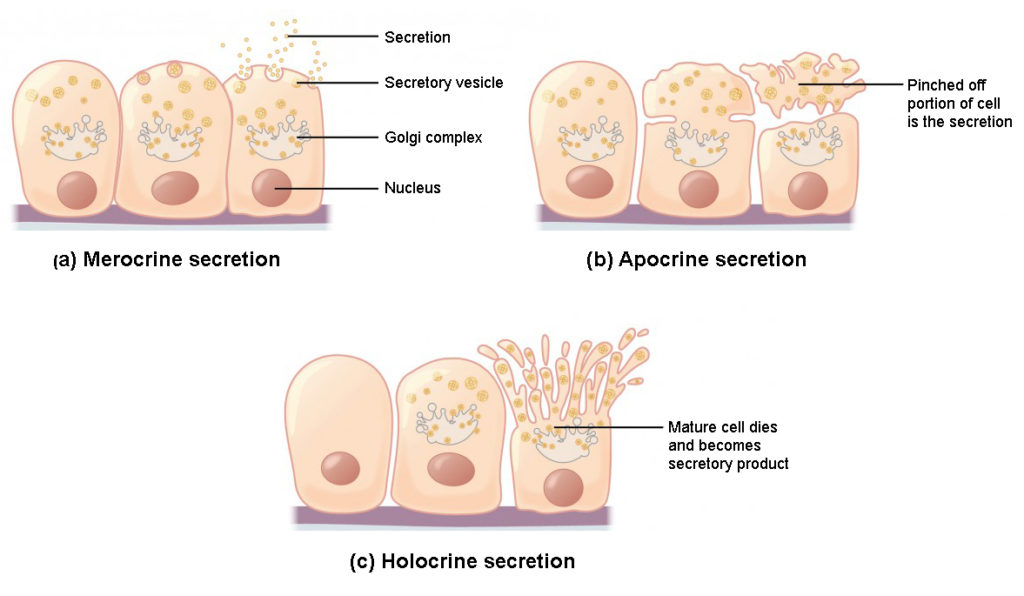



Epithelial Tissue Anatomy And Physiology I




Glands Classifications Types Functions And Diagrams Jotscroll



11 4 Endocrine System Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition




Human Endocrine System Description Function Glands Hormones Britannica




Exocrine Gland Structures Diagram Diagram Quizlet




Pineal Gland Endocrine Gland
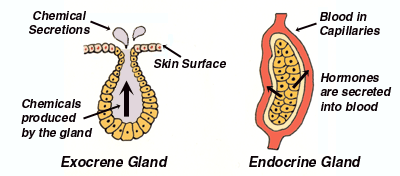



Is The Parathyroid An Endocrine Gland Are Sweat Glands Endocrine Glands Socratic



1




401 Exocrine Gland Photos And Premium High Res Pictures Getty Images




Unicellular Exocrine Glands Diagram Quizlet



Definition Exocrine Gland



15 Types Of Glands In Human Body Their Functions




Pancreas Wikipedia



Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Biology Youtube




Pin On Medical
コメント
コメントを投稿